Unit 29: Cultural Stereotypes in Media
Warm-up and Vocabulary
Hello, Class! Welcome to Unit 29. Have you ever noticed that in movies, the ‘smart kid’ always wears glasses? Or the ‘popular girl’ is always mean? These are called Stereotypes. Today, we are going to listen to lectures about these stereotypes. But we have a special mission: We are not just listening to what they say, but how they organize their ideas. Is the speaker listing types? Telling a story in steps? Or comparing two things? Let’s learn to see the ‘blueprint’ of a lecture!
Vocabulary List
Read the list below carefully. You will need these words to identify the structure of the listening passages.
- Structure: The way something is built or organized.
- Classification: Dividing things into groups or types.
- Category: A group of people or things that are similar.
- Process: A series of actions or steps taken to achieve an end.
- Cycle: A series of events that happen again and again.
- Reinforce: To make an idea stronger.
- Media: TV, movies, internet, and news.
- Villain: The bad guy in a story.
- Portray: To show or describe someone in a movie or book.
- Stage/Phase: A step in a process.
Activity 1: Let’s Discuss
Look at the questions below. Think about your answers or discuss them with a partner.
- Think about high school movies (like on Netflix). Is there always a “popular mean girl” and a “shy nerd”? Do these people exist in your real school, or are they just stereotypes?
- In action movies, how are the “villains” (bad guys) usually shown? Do they often have a specific accent or look?
- Why do you think movies use these shortcuts (stereotypes) instead of making complex characters?
How to Draw Your Notes (Mental Maps)
When a teacher speaks, they usually follow a “Blueprint.” If you identify the blueprint early, you will know exactly how to take notes.
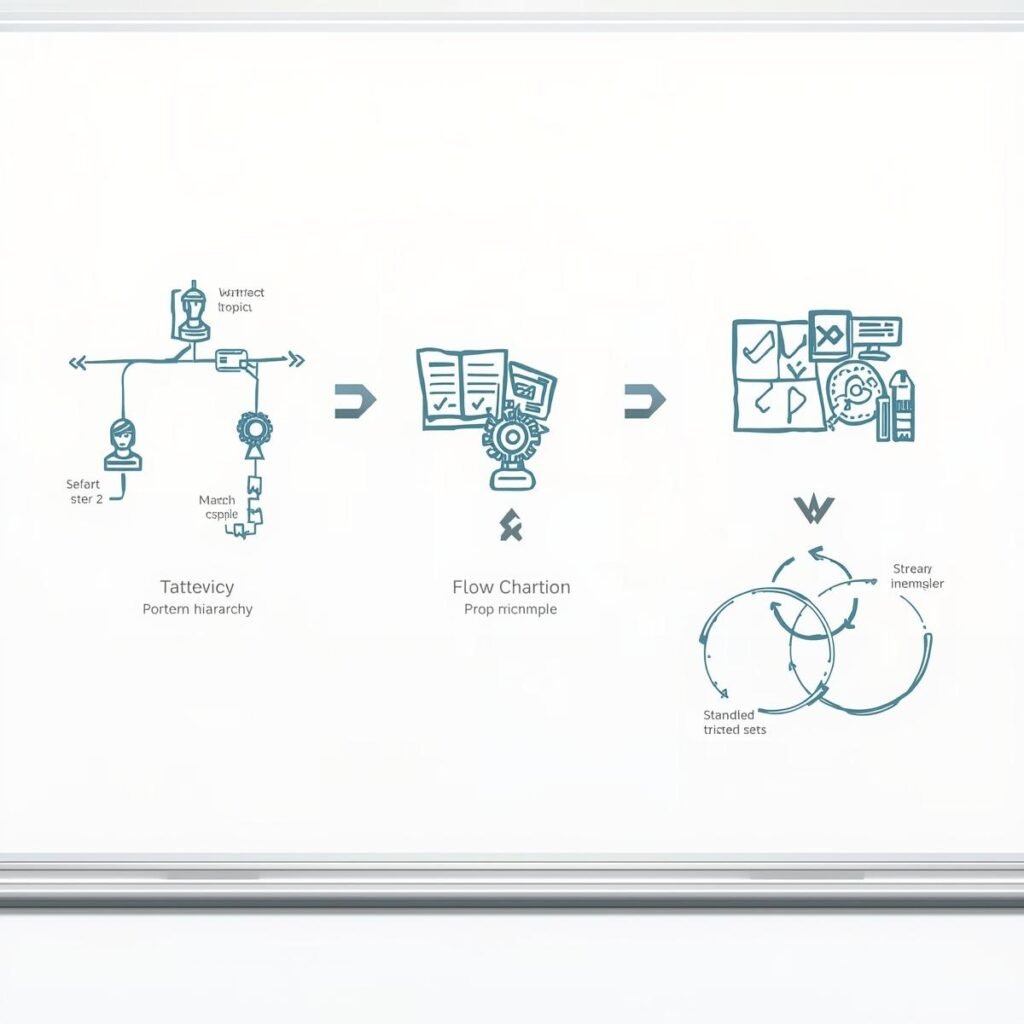
Structure 1: Classification (The “Tree” Structure)
- Concept: The speaker takes one big topic and breaks it down into smaller groups.
- Signal Words: “There are three types…”, “The first category…”, “Classes,” “Groups,” “Kinds.”
- How to Take Notes: Draw a Tree Diagram or Boxes.
- Example: Topic = Villains. Branch A = The Genius. Branch B = The Monster.
Structure 2: Process (The “Arrow” Structure)
- Concept: The speaker explains how something happens over time (Chronological order) or a cycle.
- Signal Words: “First…”, “Then…”, “Next…”, “Leads to…”, “After that…”, “The cycle begins…”
- How to Take Notes: Draw a Flowchart with Arrows.
- Example: Media Image -> Audience Belief -> Real Life Behavior.
Structure 3: Comparison (The “Balance” Structure)
- Concept: The speaker looks at two things side-by-side to show how they are the Same or Different.
- Signal Words: “Similarly…”, “Unlike…”, “In contrast…”, “On the other hand…”, “Differs from…”
- How to Take Notes: Draw a T-Chart (Two columns) or a Venn Diagram.
- Example: Column 1: Indonesian Movies (Family focus). Column 2: US Movies (Individual focus)
Skill Practice
Complete the following 4 exercises.
Exercise 1: Word Search
Exercise 2: Fill in the Structure Type
Exercise 3: Match the Note-Taking Strategy
Exercise 4: Listen for Structure
Listen to the first sentence of a lecture. Identify the structure.